
In a world brimming with data, where numbers and statistics often take the limelight, there exists an intricate realm of knowledge awaiting discovery — qualitative data analysis. Behind the scenes of quantitative measurements and figures, qualitative analysis unveils the rich tapestry of human experiences, perceptions, and emotions. It captures the nuances, the untold stories, and the intricacies that often elude quantitative methods.
While quantitative analysis aims to quantify phenomena, qualitative analysis focuses on understanding the meaning and context behind those phenomena. It offers a powerful lens through which researchers can explore diverse subjects, ranging from human behavior and social interactions to organizational dynamics and cultural practices.
Qualitative data analysis enables researchers to delve deeper into the complexities of human experiences, motivations, and beliefs, making it a valuable tool in numerous fields, including sociology, psychology, education, and market research. Let’s discuss qualitative data analysis, the steps of conducting it the right way.
Table of Contents
Understanding Qualitative Research
Now that you have a basic understanding of qualitative data analysis let’s take a closer look at qualitative research. Qualitative research is a method of inquiry that seeks to explore and understand the meaning individuals or groups attribute to a social or human problem. The primary goal of qualitative research is to gain insights into people’s thoughts, feelings, and behaviors in various contexts. This research approach allows you to examine phenomena in depth, providing a richer and more comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.
Unlike quantitative research, which is objective and focuses on measuring variables and testing hypotheses, qualitative research is subjective and emphasizes the importance of context and interpretation. As a researcher, you will be working with a qualitative research company, you will be expected to immerse yourself in the data, engage with participants, and reflect on your own experiences and biases to understand the phenomenon being studied.
Steps in Qualitative Data Analysis
Doing a qualitative data analysis for a project can be a daunting task, but breaking it down into manageable steps will facilitate the process. Here are the key steps involved:
1. Data Collection
The first step in qualitative data analysis is data collection. This involves gathering information from various sources, such as interviews, focus groups, observations, and documents. As a researcher, you will need to be intentional and strategic in your data collection efforts, ensuring that you gather rich, detailed, and relevant data that aligns with your research objectives.
During the data collection phase, it is crucial to be organized and systematic in your approach. This includes taking detailed notes, recording interviews and observations, and managing your data effectively. Remember that data collection is an iterative process, and you may need to revisit your data sources multiple times to ensure you have captured all relevant information.
2. Data Organization
Once you have collected your data, the next step is data organization. This involves sorting, categorizing, and arranging your data in a way that facilitates analysis. Data organization is crucial in qualitative data analysis, as it helps you identify patterns, themes, and relationships within your data.
To organize your data, you can use various tools and techniques, such as creating data tables, using software for qualitative data analysis, or manually organizing your data using physical materials like index cards. Regardless of the method you choose, the goal is to create a system that allows you to easily access, manage, and analyze your data.
3. Data Coding
After organizing your data, the next step is data coding. In this phase, you will assign codes or labels to segments of your data, such as words, phrases, sentences, or images. These codes serve as a way to condense and categorize your data, making it easier to identify patterns, themes, and relationships.
Coding your data is an iterative process that involves multiple rounds of coding, revising your codebook, and refining your codes as needed. As you become more familiar with your data, you may discover new themes or need to revise existing codes to better capture the nuances of your data.
4. Data Interpretation
Once you have coded your data, the next step is data interpretation. This involves analyzing your coded data to make sense of the patterns, themes, and relationships you have identified. Data interpretation is a critical step in qualitative data analysis, as it allows you to draw conclusions and generate insights from your data.
During the data interpretation phase, you will need to engage in critical thinking and reflection, questioning your assumptions and biases, and considering alternative explanations for your findings. You may also need to revisit your data, recode segments, or collect additional data to ensure your interpretations are grounded in the data.
5. Reporting and Presenting Findings
The final step in qualitative analysis is reporting and presenting your findings. This involves communicating your insights, conclusions, and recommendations in a clear, concise, and engaging manner. Depending on your audience and purpose, you may need to present your findings in various formats, such as a written report, an oral presentation, or a visual display.
When reporting your findings, it is essential to provide evidence from your data to support your conclusions and demonstrate the credibility and trustworthiness of your analysis. You should also be transparent about your research process, discussing your data collection methods, coding and analysis strategies, and any limitations or challenges you encountered.
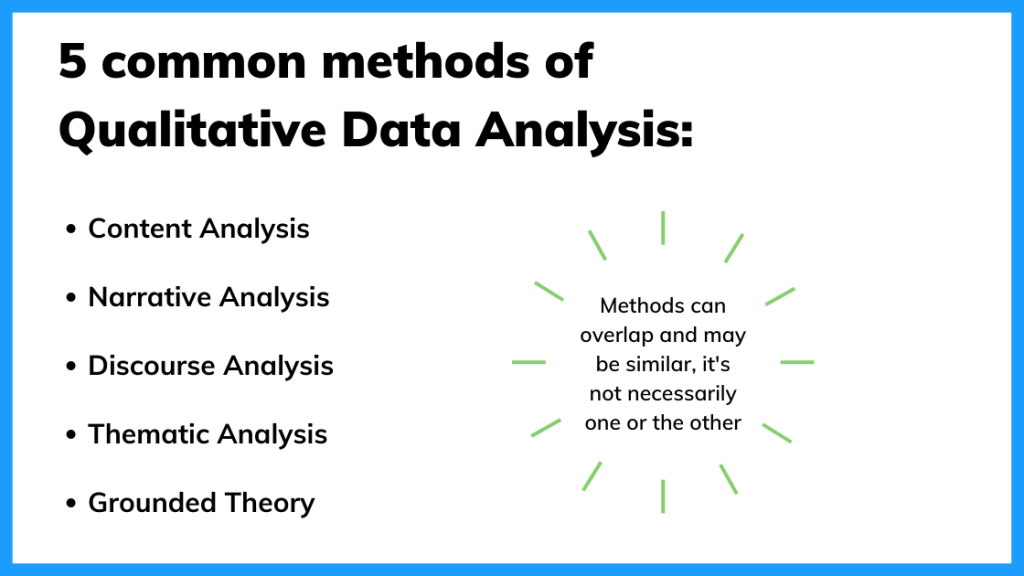
Qualitative Data Analysis Techniques
There are numerous qualitative data analysis techniques available to help you make sense of your data. Some popular techniques include:
Thematic analysis
This technique involves identifying and analyzing patterns or themes within your data. Thematic analysis is a flexible and versatile approach that can be adapted to various research questions and data sources.
Content analysis
This technique focuses on the systematic and objective analysis of text or other forms of communication, such as images or videos. Content analysis involves coding and categorizing your data based on predefined categories or themes.
Grounded theory
This technique involves generating theory from your data through an iterative process of data collection, coding, and analysis. Grounded theory seeks to capture the underlying social processes and relationships within your data.
Narrative analysis
This technique focuses on the stories individuals tell about their experiences and how these stories are structured, ordered, and interpreted. Narrative analysis is particularly useful for understanding the meaning and significance of personal experiences
Tips for Successful Qualitative Data Analysis
Now that you have a better understanding of the steps and techniques involved in qualitative data analysis, here are some tips to help you succeed in your analytical journey:
Be open-minded: Approach your data with curiosity and a willingness to explore multiple perspectives and interpretations.
Be systematic and organized: Develop a clear plan for your data collection, organization, and analysis, and maintain meticulous records throughout your research process.
Be reflexive: Reflect on your own experiences, biases, and assumptions, and consider how these may influence your data collection and analysis.
Engage with others: Seek feedback from colleagues, mentors, or other researchers to gain fresh insights and perspectives on your data and findings.
Be patient and persistent: Qualitative data analysis is a complex and time-consuming process, so be prepared to invest time and effort into your research.
Partner With the Experts of Qualitative Research
Qualitative data analysis is a powerful tool for understanding the complexities of human experiences, motivations, and beliefs. By following the steps outlined in this article and applying some of the techniques and tips shared, you will be well-equipped to embark on a successful data analysis journey.
To get the most out of your qualitative research, you should get in touch with the leaders of market research at Insights Opinion. With the help of our incredibly dedicated and skilled researchers, Insights Opinion conducts qualitative business research to determine the genuine market landscape and evaluate difficult prospects. They can assist you in understanding the underlying reasons and thoughts about marketing campaigns and products by providing detailed data from worldwide market research. Get in touch with them today to know more about how qualitative data analysis can benefit you.





More Stories
The Spark Shop – Online Shopping Big Discount: Your Ultimate Shopping Destination
TheSpark Shop Kids Clothes for Baby Boy & Girl: A Trendy Choice for Little Ones
The Ins and Outs of Knowledge Management (KM)